Layers of the Atmosphere
Let’s understand about the layers of the atmosphere and composition of the Earth's atmosphere.

What is Earth’s Atmosphere?
A thin layer of gases surrounds the Earth called the ATMOSPHERE.
The Earth’s atmosphere is like a blanket that protects life to survive in many ways. It absorbs the right amount of heat from the Sun to keep our planet at a survival temperature. It also protects us from harmful radiation.
Composition of Atmosphere
The earth’s atmosphere is mostly made up of GASES and AEROSOLS.
GASES: It contains roughly: 78% nitrogen, 21% oxygen, and 1% other gases, including argon, carbon dioxide, water vapour, carbon monoxide, Ozone (toxic gas), methane, hydrogen, etc. This mixture of gases is commonly known as AIR.

Each gas plays a vital role in the environment.
- Humans and animals need oxygen to breathe,
- Plants use carbon dioxide,
- Ozone protects the Earth from the Sun’s ultraviolet (UV) radiation.
Currently, the Earth’s temperature has been increased due to the greenhouse effect which is caused by increased levels of carbon dioxide and other pollutants.
This is called GLOBAL WARMING or GLOBAL CLIMATE CHANGE. This is the greatest threat to our home planet.
AEROSOLS: These are the tiny particles or droplets floating in the atmosphere. Aerosoles can be natural as well as human-created.
Salt evaporated from oceans, fog, mist, pollen, ash from volcanoes, etc., are examples of natural aerosols.
Forest exudates, geyser steam, cars, burning fossil fuel, and many other pollutions are examples of human-made aerosols. If you want to know more about Aerosols, we would recommend CDC.
Related Article: Earth Facts
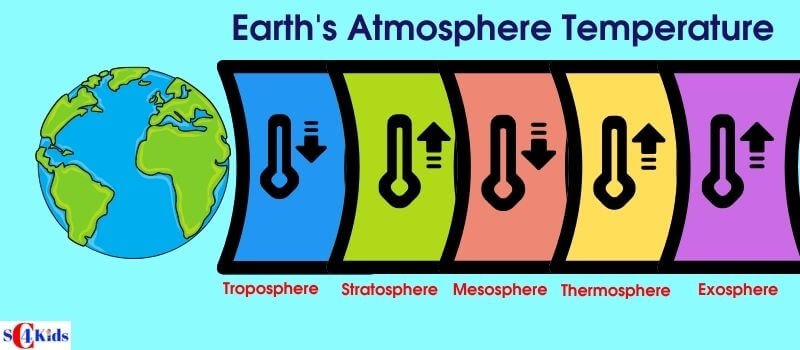
FIVE Layers of the Atmosphere
The atmosphere is divided into FIVE different layers, based on temperature. Let’s look at each, from closest to farthest from the Earth.
Troposphere
Stratosphere
Mesosphere
Thermosphere
Exosphere

1. Troposphere (0 -12 km from the ground)
➤ The word Troposphere is derived from the Greek words “tropos” means “turn, turn toward, change” and “sphere” means “as in the Earth,“
➤ This is the lowest part of the atmosphere – the part we live in.
➤ It contains most of our weather – clouds, rain, snow.
➤ It begins at the surface of the Earth and extends out to about 13 km (8.1 mi; 43,000 ft).
➤ The temperature of the Troposphere gets colder with height by about 6.5°C per kilometre.
➤ It contains most of the air molecules.
➤ It contains 75% of the atmosphere’s mass and 99% of the total mass of water vapour and aerosols.
➤ The PLANETARY BOUNDARY layer is the lowest part of the Troposphere, where temperature, moisture, and the wind is influenced by friction.
➤ The TROPOPAUSE is the top most of the Troposphere, which is the border between the Troposphere and Stratosphere.
➤ The troposphere layer can be accessed by propeller-driven aircraft.
Related Article: Why We Have Seasons
2. Stratosphere (12 - 50 kilometers )

➤ The second layer of the Earth’s atmosphere, stratosphere extends upwards from the tropopause to about 50 km.
➤ The OZONE layer is located at the top of the stratosphere.
➤ The ozone layer absorbs the UV radiation of the sun and increases the temperature of this layer.
➤ Stratosphere layer is free from any weather associated air turbulence.
➤ Most jets and large airplanes fly in the lower stratosphere to avoid turbulence in the troposphere.
➤ The Stratosphere (2nd layer) is separated from the Mesosphere (3rd layer of the atmosphere) by the atmospheric boundary known as the STRATOPAUSE.
3. Mesosphere (50 - 80 kilometers )
➤ The Mesosphere (“Meso” means middle) is the middle layer of the atmosphere that lies between the thermosphere and the stratosphere.
➤ The higher you go in the mesosphere, the temperature gets colder.
➤ The top of the mesosphere is the coldest part of the Earth’s atmosphere.
➤ Meteors burn up in this layer. A “shooting star” is a meteor burning in the mesosphere.
➤ The Mesosphere (3rd layer) is separated from the Thermosphere (4th layer of the atmosphere) by the atmospheric boundary known as the MESOPAUSE.
4. Thermosphere (80 - 700 kilometers)
➤ The Thermosphere (“Thermo” means heat) is the 4th layer of the atmosphere from the Earth’s surface.
➤ The Thermosphere is the “hottest layer” in the atmosphere as it absorbs X-rays and UV radiation of the sun.
➤ The temperature in this layer can reach up to 1500 degrees Celsius.
➤ The Thermosphere is home to the International Space Station as it orbits Earth.
➤ Aurora and satellites occur in this layer.
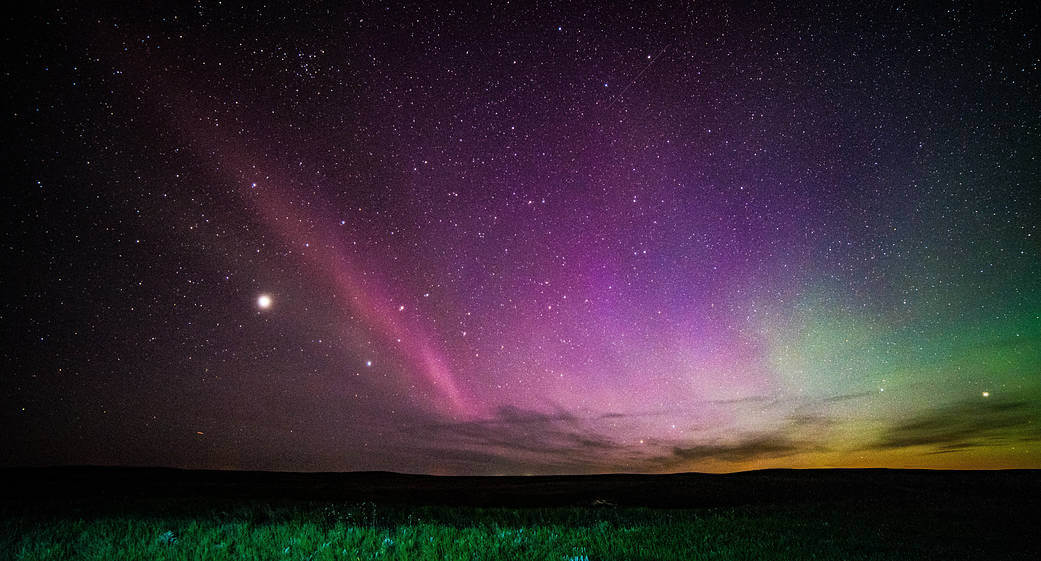

➤ The Thermosphere layer protects us from space debris coming towards Earth by burning up with its high temperature.
➤ The Thermosphere (4th layer) is separated from the Exosphere (5th layer of the atmosphere) by the atmospheric boundary known as the THERMOPAUSE.
5. Exosphere (700 - 10,000 kilometers)
➤ The Exosphere (“Exo” means outside) is the outermost layer of the atmosphere.
➤ This layer is mainly made up of low-density gases like hydrogen and helium.
➤ Atoms and molecules of these gases escape into space and usually do not collide with each other.
➤ Without a single collision, these particles can travel hundreds of kilometers.
➤ Many of the satellites orbit the earth in this layer.
In Summary - Layers of the Atmosphere
- TROPOSPHERE – closest layer to the Earth’s surface in which all weather and season occurs.
- STRATOSPHERE – Second layer of the atmosphere, where OZONE layer is located. Most jets and large airplanes fly.
- MESOSPHERE – Middle layer of the atmosphere, where most meteors burn up after entering Earth’s atmosphere.
- THERMOSPHERE – Fourth layer of the atmosphere. It is known as the HOTTEST LAYER in the atmosphere. Thermosphere is a home to the International Space Station.
- EXOSPHERE – Outermost layer of the atmosphere. Many of the satellites orbit the Earth in this layer.
