Types of Energy
Have you ever wondered how a light turns on, how your body moves, or why the sun feels warm? The answer is energy! We use energy every single day—to run, eat, play, and learn.
In this fun and easy guide, we’ll explore the 8 main types of energy, like kinetic, thermal, sound, and more. You’ll see real-life examples and learn how each type helps make the world around you work like magic!
Let’s dive in and discover the different types of energy that power our lives!
What is energy?
Energy is the ability to do work or make things happen. Everything we do—running, jumping, heating, lighting, or moving—uses energy.
Let’s explore the main types of energy and how we use them every day!
What are the 8 types of energy?
- Kinetic Energy
- Potential Energy
- Chemical Energy
- Electrical Energy
- Heat Energy
- Light Energy
- Sound Energy
- Nuclear Energy

1. Kinetic Energy—Energy of Moving Things
🔍 Examples of kinetic energy:
- A child sliding down a slide
- A puppy running in the park
- A spinning top or bicycle in motion
- A flying bird
- A speeding car
2. Potential Energy – Energy That Is Stored
Examples of potential energy:
- A stretched slingshot ready to launch
- A roller coaster at the very top before it goes down
- A swing pulled back and ready to let go
3. Chemical Energy – Energy Inside Food and Fuels
Examples of chemical energy:
- Eating a banana before soccer practice
- A battery making a toy robot move
- Burning wood in a campfire
4. Electrical Energy—Energy That Powers Things
Examples of electrical energy:
- Plugging in your tablet or phone
- Turning on a video game console
- Watching a cartoon on TV
5. Thermal Energy – Heat Energy
Examples of heat energy:
- Hot chocolate warming your hands
- A campfire or toaster heating up
- The sun warming your face outside
6. Light Energy—Energy We Can See
Examples of light energy:
- Turning on a lamp when it’s dark
- The sun rising in the morning
- A flashlight during a power cut
7. Sound Energy—Energy We Can Hear
Examples of sound energy:
- A guitar string being plucked
- Clapping hands during music class
- Barking dog or a ringing bell
8. Nuclear Energy – Energy Inside Atoms
Examples of nuclear energy:
- The sun shining every day is using nuclear energy
- Big power plants that give electricity to cities
Types of Energy Review Chart
| Energy Type | What It Means | Easy Example |
|---|---|---|
| Kinetic | Moving energy | A ball rolling, kid jumping |
| Potential | Stored energy | A bow pulled back, water in dam |
| Thermal | Heat energy | Hot soup, the sun, oven |
| Light | Energy we can see | Flashlight, sunlight |
| Sound | Energy we can hear | Bell ringing, drum beating |
| Electrical | Energy that powers things | Phone charging, TV |
| Chemical | Energy in food and batteries | Eating, batteries, gasoline |
| Nuclear | Energy inside atoms | The sun, power plants |
🔁 What Is the Law of Conservation of Energy?
The Law of Conservation of Energy says that energy cannot be created or destroyed. It can only be changed from one form to another.
When you eat food (chemical energy), your body changes it into kinetic energy when you move, and thermal energy to keep you warm!
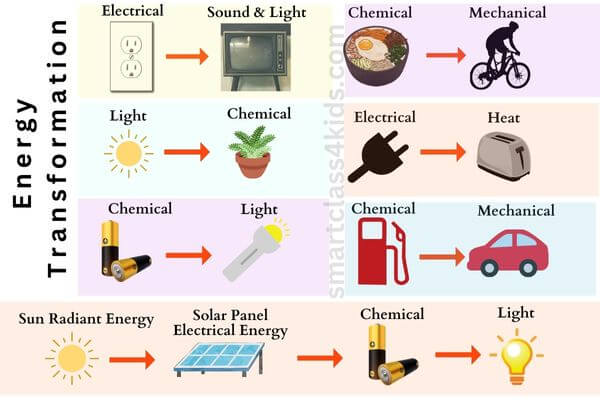
Learn how energy changes form in our Energy Transformation for Kids lesson.
Do you want to test your knowledge? Here is the Types of Energy Quiz!
