Layers of the Earth
Today we will explore different layers of the Earth: crust, mantle, and core. Let's begin to spill out all the layers of the Earth one by one.
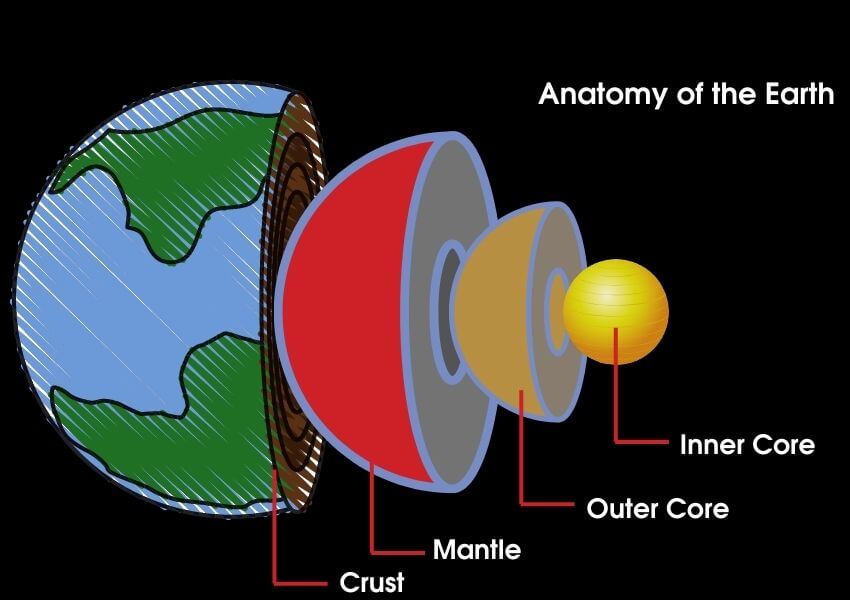
The Earth is composed of four different layers:
- The crust (1 percent of Earth’s volume)
- The mantle (84 percent)
- The liquid outer core
- The solid inner core (combinedly 15 percent).
Earth's Crust
The Crust is the OUTERMOST and THINNEST layer of the Earth where we live. Earth’s crust is about 19 miles (30 km) deep on average on land. At the bottom of the ocean, the crust is still about 3 miles (5 km) deep. (According to spaceplace.nasa.gov).
The crust of the Earth is composed of various chemical elements, minerals, or rock types.
The most common chemical elements are oxygen, silicon, aluminum, iron, calcium, potassium, sodium, and magnesium.
The most common rocks are Igneous rocks (granite, basalt), Metamorphic rocks (gneiss, amphibolite), Sedimentary rocks (sandstone, shale, limestone).
More than 90% of the crust is composed of silicate minerals.
Related Article: Layers of the Atmosphere
There are two types of crust: CONTINENTAL CRUST and OCEANIC CRUST.
CONTINENTAL CRUST: The Earth’s outer rocky layer, made up of rocks that consist primarily of silica and alumina called the “sial“.
OCEANIC CRUST: below the continental crust, composed of dense rocks, primarily the igneous rock basalt
The boundary between the crust and underlying mantle is termed the Mohorovicic discontinuity, often referred to as the Moho.
Did You Know? The oldest rocks on our planet are part of the continental crust and date back approximately 4 billion years in age.
Earth's Mantle
The mantle is the LARGEST LAYER of the earth that lies beneath the crust. It represents 84% of the Earth’s volume.
The mantle goes 1,800 miles (2,900 km) deep. This layer is composed of very hot, dense rock, rich in the chemical elements magnesium, silicon, and oxygen.
In the upper mantle, temperatures range between 500 to 900 °C (932 to 1,652 °F). In the lower mantle, temperatures can reach over 4,000 °C (7,230 °F).
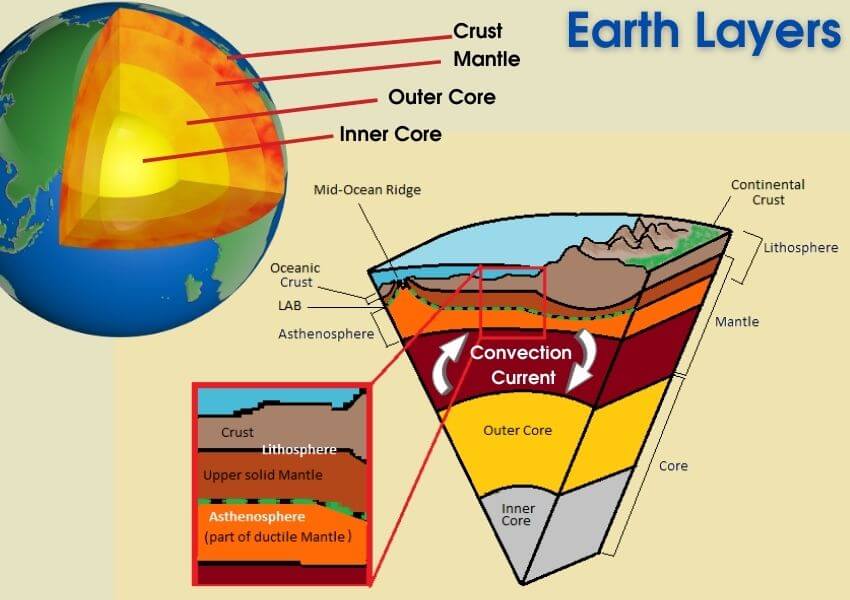
Tectonic Plates:
The tectonic plates are a combination of the crust and the uppermost part of the mantle, also called the LITHOSPHERE.
These plates have irregular shapes and fit together, just like puzzle pieces.
Areas where the edges of plates touch each other, are called PLATE BOUNDARIES. Most natural events, including volcanoes, earthquakes, and mountain building, take place at plate boundaries.
The mantle has an incredibly dense, hot, thick material that slowly circulates in giant CONVECTION CURRENTS, which drag the crust around.
Know More About: Plate Tectonics
Related Article: The Water Cycle
What are convection currents::
Convection is a heat transfer process. Convection currents transfer heat from one place to another by mass motion of a fluid or gas particles. Boiling water in a pot is a good example of convection currents.The boundary between the base of the mantle and the outer core is termed the GUTENBERG DISCONTINUITY.
Earth's Outer Core
The outer core is composed mostly of the melted metals nickel and iron. It is about 1400 miles (2253 km) thick, and its average temperature is 9,000 F (5,000 Celsius).
It is the movement of the liquid within the outer core that generates Earth’s magnetic field.
Earth's Inner Core
The inner core is an extremely hot ball of solid metal, composed mainly of iron and nickel.
While the inner core is hotter than the outer core, still iron and nickel remain solid in this layer. It is solid because the inner core is under an incredible amount of pressure (over 3 million times greater than on Earth’s surface) from the rest of the layers on top of it.
It is about 1,585 miles (2,550 km) across, and the temperature is about 10,800 F (6,000 C). The inner core is the hottest part of the Earth, as hot as the sun’s surface.

Layers of the Earth Activity – Make a Fan with Earth’s Layers
In Summary - Layers of the Earth
1. The Crust
- It is the OUTER layer and THINNEST portion of the Earth.
- It is made up of solid rocks and minerals.
- There are TWO types of crust: CONTINENTAL and OCEANIC crust.
- Oceanic crust – Basalt
- Continental crust – Granite
- Oceanic crust is more dense than continental crust.
- The boundary between the crust and underlying mantle is termed the Mohorovicic discontinuity, often referred to as the Moho.
3. The Outer Core
- It is composed mostly of the melted metals nickel and iron.
- Movement of the liquid within the outer core generates Earth’s magnetic field
2. The Mantle
- It is the LARGEST layer of the earth that lies beneath the crust.
- It represents 84% of the Earth’s volume
- This layer is composed of very hot, dense rock, and rich in the chemical elements.
- Top portion of the mantle is called the ASTHENOSPHERE.
- Density increases with depth due to increasing pressure.
- The boundary between the base of the mantle and the outer core is termed the Gutenberg discontinuity.
4. The Inner Core
- It is an extremely hot ball of solid metal, composed mainly of iron and nickel.
- The inner core is the hottest part of the Earth.
→ Now it’s your turn – Attempt the Layers of the Earth Quiz.
Layers of the Earth Frequently Asked Questions - FAQs
What is the outer layer of the Earth?
The CRUST is the outer layer of the Earth.
What are the different layers of the Earth?
The different layers of the Earth are the crust, mantle, outer core, and inner core.
What are the two types of Earth's crust?
Continental crust and oceanic crust are the two types of earth's crust.
What is the hottest layer of the earth?
The inner core is the hottest layer of the earth.
What is the largest layer of the earth?
The Mantle is the largest layer of the earth.
What is the thinnest layer of the earth?
Crust is the thinnest layer of the earth.
What are Tectonic Plates?
The tectonic plates are a combination of the crust and the uppermost part of the mantle, also called the lithosphere.
