The Plant Life Cycle for Kids: Learn Every Stage Step-by-Step
What is the Plant Life Cycle?
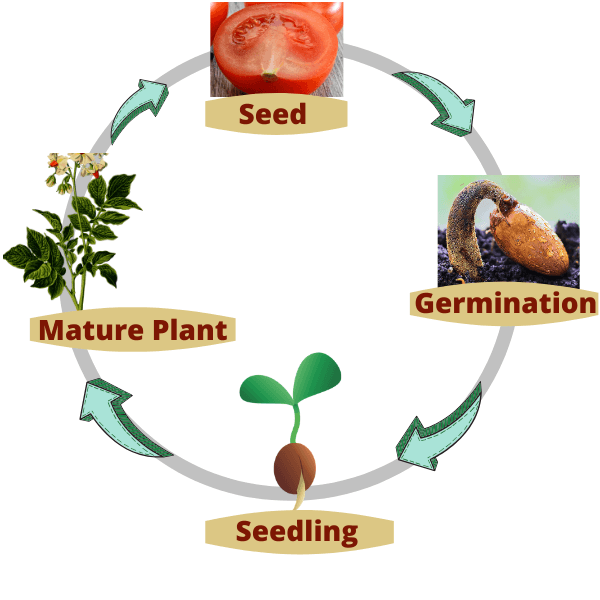
The plant life cycle is the journey every plant takes—from a tiny seed to a big plant that makes new seeds. It’s a circle that starts, grows, and starts again. It’s called a cycle because it keeps repeating—just like the hands of a clock go round and round.
Every plant goes through the same basic stages: it starts as a seed, grows into a plant, makes flowers or cones, and creates new seeds to grow again.
A seed is like a baby, the plant is the adult, and the flower is like a parent that helps make new babies (seeds) again!
However, not all plants produce seeds. Some plants, such as ferns or mosses, produce different kinds of cells called “Spores”. These plants do not produce seeds.
Bananas contain a natural chemical which can make people feel happy.
Let’s understand more about the plant life cycle for kids. If you’re short on time or finding it difficult to understand some topics like plant biology clearly, buying research papers from trusted academic sources can sometimes help guide your learning and improve your knowledge by providing solid examples or references for your assignments. Always use these resources responsibly to support your studies.
✍ Different Stages of a Plant Life Cycle
Seed
Germination
Seedling
Adult Plant
Pollination
Seed Dispersal
1. Seed – The Beginning of Life
A seed holds the tiny baby plant inside. It also has food stored around it to help the plant start growing.
Most seeds are asleep or dormant—waiting for the right moment to wake up.
💡 Example: Beans, sunflower seeds, and even acorns are all seeds.
🧠 Fun Fact: Some seeds can stay asleep for hundreds of years and still grow when planted!
Seeds wait to germinate until three needs are met: water, correct temperature (warmth), and a good location (such as in soil).
👉 Learn more about seed growth and the plant kingdom to explore how plants differ from other life forms.
Seed > Germination


2. Germination – Wake-Up Time!
Germination is the moment the seed wakes up and begins to grow.
When the seed gets:
- Water
- Warmth
- Air
…it breaks open and sends out a root to hold itself in the ground. Next, a little green shoot pushes upward toward the sunlight! The process of the sprouting of seed usually after a period of dormancy is called germination.
Seed > Germination > Seedling
3. Seedling – A Baby Plant
The seedling is like a baby learning to stand up.
It has:
- A small stem
- A few tiny leaves
- Little roots just beginning to grow
This is when the plant starts photosynthesis, which means using sunlight + water + air = plant food (glucose)!
💡 Example: Baby tomato plants or green sprouts.
📎 Learn more about photosynthesis.
👉 Check out the stages of a seed’s development in our plant life cycle quiz and test your knowledge!
Seed > Germination > Seedling > Adult Plant
4. Adult Plant – Full Grown and Strong
The seedling keeps growing until it becomes an adult plant. Now it has:
- Big leaves
- Strong stems
- A full root system
The plant is strong enough to make flowers, which means it’s ready to start the next generation.
Example: A sunflower or bean plant in your garden!
Seed > Germination > Seedling > Adult Plant > Flowering & Pollination
5. Flowering and Pollination – Time to Make Seed

Most plants use flowers to make seeds. Inside the flower are tiny parts that make pollen. When pollination happens (pollen moves from one flower to another), a seed can begin to grow.
Pollen is transferred by different pollinators, such as:
- Bees
- Butterflies
- Wind
- Birds
When a butterfly or another pollinator visits a flower, tiny grains of pollen stick to its legs like golden dust. As it flutters to the next flower, it gently carries the pollen and brushes it onto the pistil—the special part of the flower that receives it.
This magical process is called pollination.
Once pollination happens, the flower begins to grow seeds, starting a brand-new life cycle!
📎 Explore parts of a flower and how pollination works
6. Seed Dispersal – Spreading the Seeds
Once the seeds are made, they need to travel to a new place to grow. This is called seed dispersal, and it can happen in fun ways:
- Carried by animals or hidden by squirrels
- Blown by the wind like a dandelion
- Carried by water, like a floating coconut
- Stuck to a person’s shoe or clothing
Now the new seeds fall into the ground, and the plant life cycle begins again!
The fruit of the dynamite tree (also known as the sandbox tree) explodes with a loud bang, firing seeds 100 ft away.
What are seedless plants?
The plants that do not produce the flowers and seeds to reproduce are called seedless plants. Such as ferns or mosses produce different kinds of cells called “Spores”.
Spores are the part of the plants or their remains. Spores produce new plants, which continue to grow.
👉 Learn more about how spore-producing plants fit into the broader biological kingdoms.
Plant Life Cycle Vocabulary for Kids
| Word | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Seed | The beginning of a plant |
| Germination | When a seed wakes up and starts to grow |
| Seedling | A baby plant |
| Photosynthesis | The way a plant makes food from sunlight |
| Pollination | Moving pollen to help plants make seeds |
| Seed Dispersal | How seeds travel to new places |
✍ Summary - Plant Life Cycle

Amazing Plant Life Cycle Facts
- 🌻 Sunflowers turn their heads to follow the sun all day!
- 🥥 Coconuts are seeds that can float across oceans.
- 🐦 Birds poop out seeds that grow into trees!
- 🍓 Strawberries have their seeds on the outside.
📌 Frequently Asked Questions
What is the life cycle of a plant in simple words?
What are the 6 stages of a plant's life cycle?
- Seed
- Germination
- Seedling
- Adult Plant
- Pollination
- Seed Dispersal.
What is germination and why is it important?
Which plants grow from spores instead of seeds?
We hope you enjoyed learning about the plant life cycle for kids!
👉 Don’t forget to try the quiz on the plant life cycle to test your understanding!
