The Nervous System
What is the Nervous System?
The nevous system is very important to the body. The nervous system is a complex network of billions of nerve cells, (or neurons) that gathers and relays information about your surroundings to your brain.
The nervous system carry messages between our brain and spinal cord to various parts of the body. It is made of the Brain, Spinal Cord, Nerves and all the sensory organs
The nervous system is the major controlling and communicating system in the body. Our nervous system is responsible for all the mental activity such as thinking, learning, and memory.
What is the difference between NEURON and NERVE?
What is Nerve?
Nerves are the bundles of neurons or nerve cells that start at the brain and branch out to the rest of the body parts.What is Neuron?
The neuron (also known as nerve cell) is the smallest worker (basic unit) in the nervous system. It sends and receives electrical signals.
The neuron is made up of a cell body called dendrites and a threadlike structure named axon. Dendrites bring electrical signals to the cell body and axons take information away from the cell body.
Types of Nerves
There are three types of nerves in the human body, sensory nerves, motor nerves and mixed nerves.
Sensory Nerve
It is also known as afferent nerves, send messages to the brain or the spinal cord from the sense organs.
Motor Nerve
Motor nerves carry the messages in the form of a response from the brain or the spinal cord to other parts of the body such as the muscles and glands.
Mixed Nerve
Mixed Nerves perform both the action of sensory nerves as well as a motor nerve. They transform electrical impulses from the central nervous system to the muscles of the body.
Structure of a Nerve
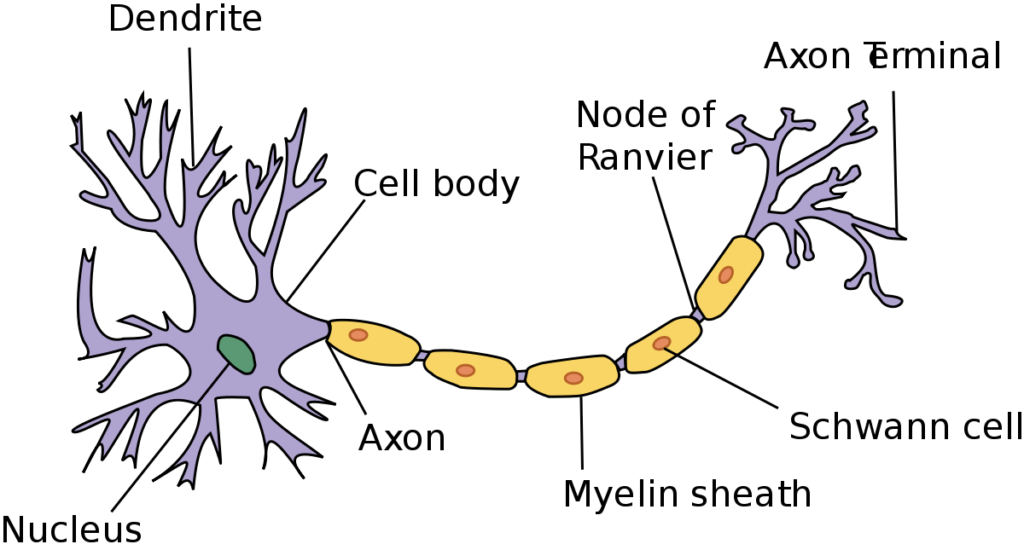
Soma (Cell Body)
The main role of the soma is to receive information. The cell body contains the nucleus and cytoplasm.Axon
This is the threadlike structure attached to the cell body. The axon transmits information to muscles, glands and other neurons.Dendrites
Another threadlike structure extending from the neuron cell body and carrying information from other neurons to the soma. At synapse, a neuron communicates with another neuron.What is the difference between Axons and Dendrites?
Axons
- Axon carries information away from the cell body.
- There is only one axon attached to each neuron.
- Axon surface is smooth.
- Axons are much longer than Dendrites
Dendrites
- Dendrites bring information to the cell body.
- Whereas a neuron can have many dendrites
- Dendrites are rough
- Dendrites are shorter in appearance.
How Nerve Cells Work Step By Step?
Neuron communicates with another neuron at a point called Synapses. The point at which the Axon terminal of a neuron meets the dendrites tip of another neuron called synapses. There are so many tiny gaps that hold chemicals, called neurotransmitters.
Neurotransmitter chemicals transmit nerve impulses from one nerve to another or from nerves to muscle cells.
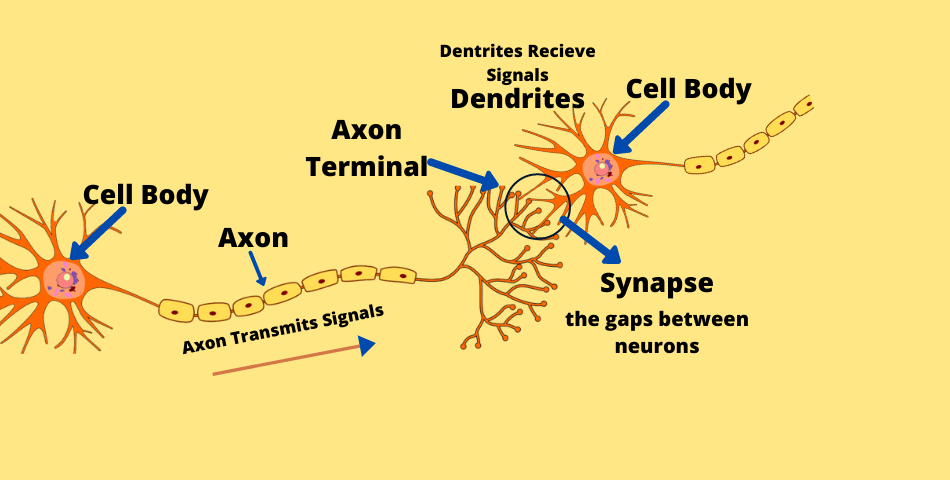
STEP 1. ➤ A Dendrites receive an impulse (signal) from another neuron, and they transmit the signal to the cell body.
STEP 2. ➤ From the cell body, an impulse (signal) transmits to the synapse through the axon. Once an impulse reaches the synapse, the axon releases a neurotransmitter chemicals from tiny gaps at the end of the nerve cell. This chemical helps the message reach the next neuron.
STEP 3. ➤ The chemicals move along to the next neuron sparking an electrical charge which moves the nerve impulse forward, and the process begins over again.
Impulse > Dendrites > Cell Body > Axon > Synapse > Dendrites
What are the Parts of the Nervous System?
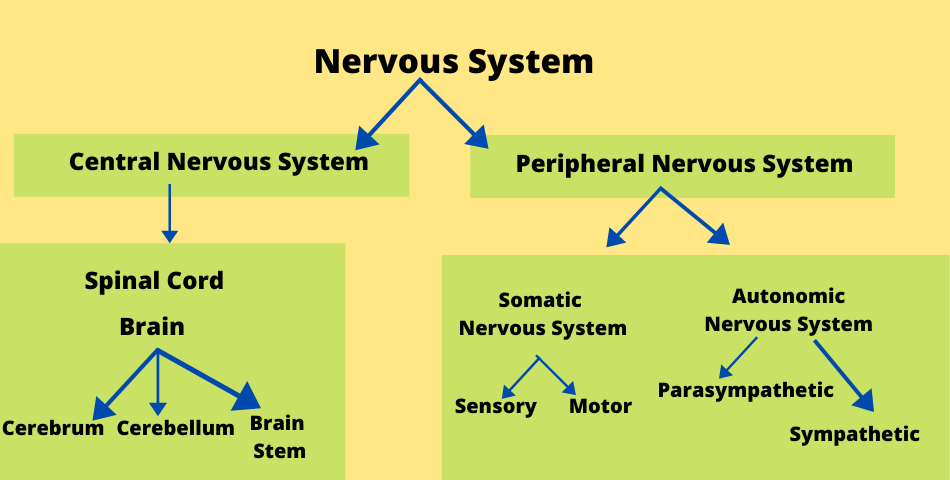
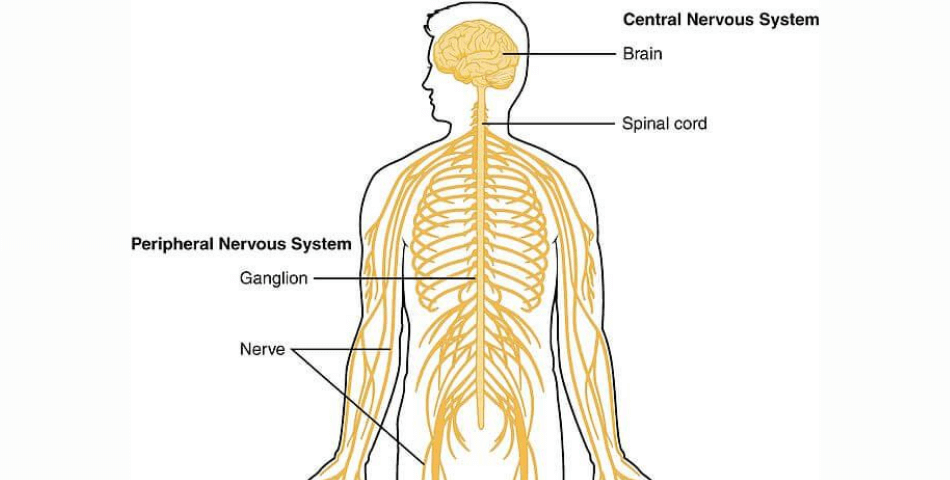
The nervous system is organised into two main parts, the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system.
THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM
It controls the functions of the body. It is referred to as “central” because it combines all the information from the entire body and coordinates activity across the whole organism.
Organs of the Central Nervous system
It consists of the brain and the spinal cord. These organs of the central nervous system are located in the center of the body.

BRAIN – The brain is protected by the skull. It controls many of the body’s functions including sensation, thought, movement, awareness, and memory by sending and receiving messages through nerves.
SPINAL CORD – The spinal cord is a long, thick bundle of nerves which runs up the middle of the back to the brain. It connects to the brain via the brain stem and then runs down through the spinal canal. The spinal cord is protected with the bony vertebrae of our backbones.
Spinal Cord Function – The spinal cord is the highway for communication between the body and the brain. The spinal cord carries information from various parts of the body to and from the brain.
THE PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM
The peripheral nervous system lies outside the central nervous system. The main function of the peripheral nervous system (PNS) is to connect the central nervous system (CNS) to the rest of the organs, limbs, and skin.
There are mainly TWO parts of the Peripheral Nervous System:
THE SOMATIC NERVOUS SYSTEM – In greek word, ‘soma’ means ‘body’. It is mainly responsible for carrying sensory and motor information to and from the central nervous system.
THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM – It is mainly responsible for regulating involuntary body functions, such as blood flow, heartbeat, digestion, and breathing.
THE HUMAN BRAIN
The brain is the most complex organ in the human body. The brain is the “Control Center Module” for our body and coordinates activity. There are around 100 billion neurons present in the human brain and they are all interneurons.
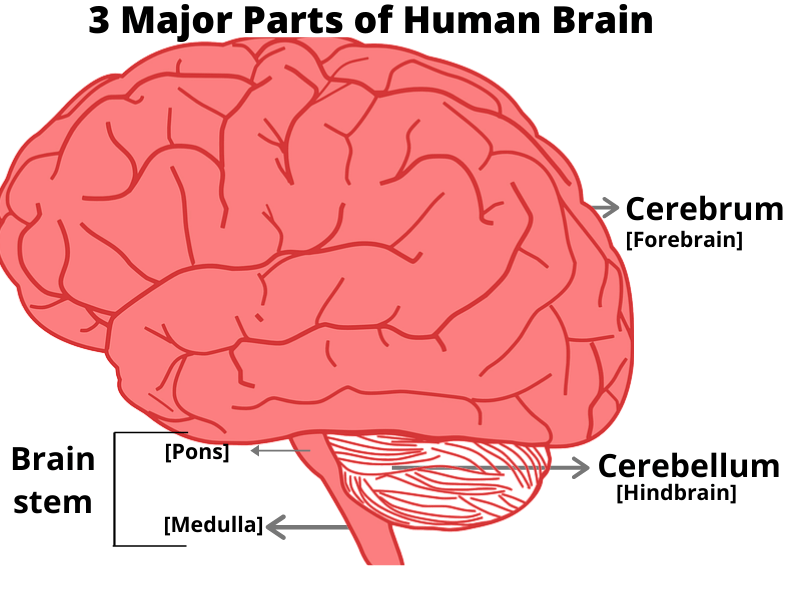
The brain has THREE main parts: THE CEREBRUM, THE CEREBELLUM and THE BRAIN STEM.
THE CEREBRUM – The cerebrum is the largest as well as uppermost part of the brain. The cerebrum controls thinking, talking, remembering, and moving. When you solve a puzzle, draw a picture, play a video game, remember some memories, or dance, you use the cerebrum.
The cerebrum is divided into TWO HALVES, called HEMISPHERES. The left hemisphere and the right hemisphere.
Each hemisphere of the brain interacts with the opposite side of the body. The left hemisphere controls the right side of the body. The right hemisphere controls the left side of the body.
Each hemisphere of the cerebrum is divided into broad regions called LOBES such as the FRONTAL LOBES, the PARIETAL LOBES, the TEMPORAL LOBES, and the OCCIPITAL LOBES.
THE CEREBELLUM – The cerebellum is the middle part of the brain located at below the cerebrum. It’s job is to help to keep your balance, maintain the posture and keep your muscles working together.
When you stand upright, keep your balance, and move around you use the cerebellum.
THE BRAIN STEM – The brain stem is located just under the cerebrum. It controls a lot of the ‘automatic‘ actions of your body such as breathing and heartbeat, and links the brain to the spinal cord and the rest of the body.
READ HERE – AMAZING BRAIN FACTS FOR KIDS
You can also read here
